Publication in ChemPlusChem
Team LTSMDeveloped by ICSM researchers, original formo-phenolic resins offer new perspectives for extracting Uranium from seawater.
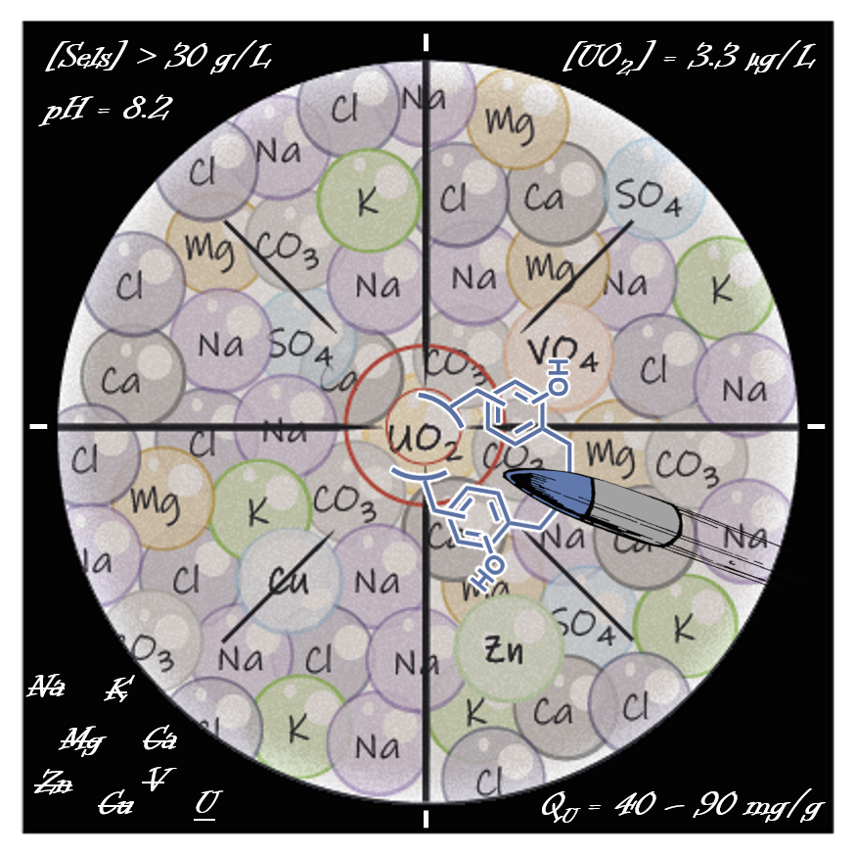
In the context of a significant worldwide deployment of nuclear energy, the limitation of traditional uranium reserves has led to an interest in exploiting unconventional reserves such as marine resources. With an average concentration of 3.3 µg L-1 in the oceans and seas, considering that these ecosystems represent more than 70% of the world's surface, nearly 4.5 billion tons of uranium are estimated in this environment, which corresponds to approximately 1,000 times the total uranium reserves present in the earth's crust. Although uranium extraction began in the 1960s, it remains a major challenge today, since the initial medium is particularly complex in terms of its chemical composition, pH, temperature, and the presence of salts and competing metals in high concentration. The adsorbents developed are organic materials containing chelating molecules of uranium, covalently incorporated by copolymerization in a formo-phenolic matrix. From seawater doped with uranium, these materials offer adsorption capacities of 40 to 90 mg per gram of resin, and are extremely selective for uranium with respect to the alkaline and alkaline-earth elements, as well as the transition metals zinc, copper, and vanadium to a lesser extent. The studies carried out have also highlighted the endothermic character of the extraction, with an increase in adsorption as a function of temperature, from 10°C to 60°C, offering prospects of interest for the extraction of the metal contained in brine from the discharge of seawater desalination plants. The uranium is then desorbed by washing the resins with sulfuric acid, and the recycled materials retain the same adsorption capacity after several reuses.
Credit: E. Lelong / ICSM
For more information, read the article by Guillaume Mossand, Evan Lelong, Chen Xing, Frantz Ndebulia Watchou, Antoine Leydier, Guilhem Arrachart, and Stéphane Pellet-Rostaing in ChemPlusChem, e202200412 (2023). DOI: 10.1002/cplu.202200412